The Art of Motivating a Group of People to Act Towards Achieving a Common Goal âââ€susan Ward
Keywords
Team Motivation, Dynamic Leadership, Leadership Way, Leadership Theories, Culture, Healthcare Sector, United Arab Emirates.
Introduction
Enquiry on leadership is becoming increasingly common among healthcare professionals (Schneider & Somers, 2006; Uhl-Bien & Marion, 2009). Scholars claim that this perspective is crucial for addressing team motivation in the context of an increasingly turbulent and apace changing healthcare services sector (Lichtenstein & Plowman, 2009; Hanson & Ford, 2010). Moreover, team motivation in cognition-intense organizations is rarely discussed due to the circuitous nature existing betwixt perspectives on leadership and organizational culture in the healthcare industry (Greenfield, 2007). Hanson & Ford (2010) discussed that the highly circuitous networks between bureaucratic organizational structures and leadership conventions interactively and mutually back up the acceleration of organizational outcomes that lead to successful team motivation (Hanson & Ford, 2010). Enacting effective leadership can drive improvements in team motivation and greatly benefit the dynamics of organizational culture in health care practices (Körner et al., 2015).
For healthcare professionals, the challenge in the composition of squad motivation is in overcoming the leadership expectations inherited while maintaining the statusquo in a multi-professional rehabilitation organization (Strasser et al., 2005). The healthcare manufacture representsa set of organisations that are conventionally shaped by the bureaucratic model, separating organisation of piece of work from commitment of piece of work (Penprase & Norris, 2005; Uhl-Bien et al., 2007). In other words, leadership is characterised bya top-downwards approach (Millward & Bryan, 2005; Murphy, 2005) to achieve maximum unit efficiency (Butler, 2008). Therefore, environments where leadership beliefs is constrained by outdated management concepts may limit critical organizational civilization dynamics that facilitate the achievement of positive team motivation. In other words, wellness care organizations gained less from spending on the efforts and resources used for improving the outcomes with the help of traditional leadership methods (Burns, 2001). In gild to improve the effect, there must be a shift from the traditional leadership models to modern leadership models.
The healthcare professionals have to come across the changing demands of the patients, therefore they should focus on catalysing the process of trouble solving, collaboration, team management and creativity, amidst others, to become central to efficacious team motivation. (Lemieux-Charles & McGuire, 2006). Successful accommodation of multi-disciplinary team motivation does not necessarily mean organizational restructuring or enhancing an individual's professional person or managerial skills and competencies. A multi-professional team level involves professionals of different disciplines who work separately in nature, only work together to achieve organizational outcomes (Epstein, 2014; Tzenalis & Sotiriadou, 2010). Team motivation in the healthcare services manufacture leads complex adaptive organizations through dynamic processes that require leaders to view both organizations and leadership from different perspectives. Hall (1999) notes that leaders need to sympathize the importance of a revolutionary management style that encompasses changes in behavioral processes, mediated by the dynamic of organisational culture that affects outcomes. These key causal relations touch the inter-departmental or ecology boundaries of the healthcare industry. Evidence suggests that leaders must counter the current leadership styles to understand the behaviour of healthcare professionals typically by transforming the corporate practices by involving the informal leaders. Further, holistic team motivation can be harnessed by increasing the organizational adaptive capacity (Uhl-Bien et al., 2007; Schreiber & Carley, 2008; Tsai, 2011; Al-Sawai, 2013).
This paper argues that nearly studies on team motivation emphasize team piece of work, linking it to chore satisfaction (Korner, 2010; Körner et al., 2015), patient safety (Manser, 2009), team climate and team efficiency (Poulton & West , 1999). Few studies have investigated the effects of dynamic leadership on the role of multi-professional team motivation in healthcare organizations. Before research on leadership has produced normative statements on how leadership should be undertaken (Oliver, 2006; Al-Sawai, 2013). Empirical studies have focusedon working with individuals (Murphy, 2005; Tsai, 2011) or at a broader organisational level (Osborn & Chase, 2007). Leadership style at the multi-professional team level has been overlooked. Much prove onorganisational culture in healthcare staff practices, values and assumptions well-nigh their piece of work is bachelor (Körner et al., 2015). Withal,thesestudies have failed to appreciate the evolution of organisational systemic dynamics thatchallengeresearch on organisational civilisation inhealthcare organizations. Furthermore, it is argued that cultural research among multi-professionalsin the healthcare setor has been neglected (Körner et al., 2015). It is necessary to explore how the dynamics of organisation civilisation determines and/or antecedes multi-professional person team motivation in healthcare organizations. Understanding how to enact constructive leadership and motivating at the multi-professional team level is an of import issue, particularly as teamwork has been shown to be neceassary for providing services in the complex healthcare manufacture (Hall, 1999; Negreiros et al., 2017). Multi-professional squad motivation in the healthcare organization requires further empirical research (Leggat, 2007; Tzenalis & Sotiriadou, 2010; Epstein, 2014). This paper presents literature review that address this issues.
This study reports literature that empirically supports the relationship between dynamic leadership and multi-professional squad motivation inhealthcare organizations, as well the mediating effect of the dynamics of organisational culture in this human relationship.
Literature Review
Motivation Theory
Motivation is an essential part of success and business prosperity in the existing dynamic and competitive marketplace. It comprises of an individual's internal characteristics and the external factors that include job factors, individual differences and organizational practices (Gopal & Chowdhury, 2014).
Motivation is the need for and expectation of work and the dissimilar factors in the workplace that facilitate squad motivation (Bahmanabadi, 2015). It is of import for managers to emerge as leaders so that they sympathise squad members' needs and expectations, which drive the organization's culture. Of all the functions that a leader performs, motivating employees is the about important and complex task (Almansour, 2012). A major reason for this is that team motivation attributes change constantly. The major factors that motivate employees are fulfilling of needs, workplace justice, labour expended, employee evolution programs and policies of reward and appreciation (Hamidifar, 2009).
Motivation in the healthcare industry can be defined as an individual'due south degree of willingness to exert and maintain the production of try towards organizational goals. Motivation is closely associated with aspects such as job satisfaction, which drives people to perform. Motivating and satisfying healthcare professionals helps to ameliorate the overall functioning and services of the healthcare system. Healthcare professionals who are poorly motivated accept a negative outcome on the entire system and private facilities (Zachariadou et al., 2013).
Motivating teams is more challenging than motivating an individual. Very often, individuals in the team take different beliefs, values and different goals and expectations. A team tin be defined as a collection of individuals who accept different skill sets; work together to achieve goals and help team members to collaboratively apply different skills (Enbom et al., 2005). Information technology is difficult for a leader to motivate every member of a team based on his or her unique motivating cistron. A single motivation strategy has to exist selected for the team so that information technology tin be motivated effectively (Clark, 2013). Moreover, motivating a team is ofttimes challenging as both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation strategies have to be determined co-ordinate to the values, beliefs and thinking of the entire team. There tin be both positive and negative personalities in a team. Positive personalities help individuals to contribute their unique capabilities and potential effectively (Clark, 2013).
People in the healthcare system may have the expertise, but if they are not motivated, they will non exist able to achieve their potential. With the relevance and importance of the squad increasing in organizations, the focus is shifting from private motivation to squad motivation. If an individual is motivated in a healthcare organization, this builds trust and motivates others, thereby improving squad motivation levels. Burton (2012) posits that non-financial rewards are more powerful motivators than financial incentives. These rewards or recognition tin can be earned individually or in teams and tend to motivate both teams and individuals. Burton states that group rewards are more than positive as they improve squad bonding, along with increasing productivity. If employees are allowed to work in teams, they get easily motivated. Moreover, the team is responsible for making of import decisions collectively and this can further improve team motivation (Burton, 2012). In healthcare organizations, motivating staff and professionals is also necessary, because nursing staff and other professionals accept to deal with high levels of stress.
Humphrey et al. (2009) define a team every bit a group of people who work actively together to achieve a common purpose and are willing to work to ensure that their objectives are achieved. In a healthcare organization, teams have prime relevance, as it is a multi-disciplinary profession, including nurses, doctors and professionals of different specialties. These people must work effectively in a team, communicating and sharing resources. Each member of a healthcare team has specialized knowledge to perform different tasks. These multi-professional teams solve health problems. Such teams course an important feature of organizations in all industries, not only healthcare. The perspective on which they are based is that all the team members are highly qualified. The potential value of such teams is clear, simply healthcare organizations are finding it difficult to motivate them, which is a challenging task. Further, motivation alone is generally not enough, other features such as communication are essential. Open interactions help team members to communicate effectively about their professions. Moreover, each member should accept the opportunity to communicate, every bit this further motivates these professionals (Rose-Grant, 2016). Leadership can never be separated from team motivation and effective leadership is associated with the durable motivation of team members.
Dynamic Leadership Theory
Social psychologist Lewin (1890-1947) divers and differentiated three major classical leadership styles. Many consider Lewin to be the founder of social psychology and management theory besides as leadership studies. Later on extensive experiments in group dynamics and leadership, he developed the concept of leadership climate. Based on this concept, Lewin divers 3 types of leadership climates: democratic, authoritarian and laissez-faire. Further, the selection of leadership style depends on the needs associated with making a conclusion. The three types of leadership styles are discussed below:
Authoritarian Leadership Style: Authoritarian leaders are distant from their employees. This type of leadership is gained through demands, punishments, regulations, rules and orders. The major functions of disciplinarian leadership fashion include assignment of tasks, unilateral decision-and rule-making and problem-solving. Followers of authoritarian leaders must adhere to all the instructions without comment or question. Authoritarian leaders brand all the decisions themselves without involving employees or followers and impose these decisions on them (Greenfield, 2007). In the long term, authoritarian leadership manner tin exist detrimental as it is dictatorial in nature. This leadership style undermines creativity and individuality considering these managers consider themselves to be right. However, the fine art of leadership is flexibility, i.due east. to suit to dynamic situations. All the same this leadership fashion also has some advantages: if at that place is urgency and a task is time critical, then one needs to have bailiwick and structure so that the job can be done speedily. In a situational leadership style, disciplinarian leadership is adopted in some circumstances (Wiesenthal et al., 2015).
Autonomous Leadership Style: This is also known every bit participative leadership style and reflects principles and processes such as self-determination and equal participation. However, democratic leaders must not be compared with those who concord elected positions. These leaders facilitate collective conclusion making, involving their followers or employees and offer them back up and choices. Further, this leadership manner, unlike the disciplinarian style, is characterized past cooperation, active participation, accountability and delegation of responsibilities and tasks. A major function of democratic leadership is empowerment of subordinates, distribution of responsibility and facilitation of grouping deliberations. Followers are held answerable for their decisions, actions and willingness to maintain the group'due south freedom and autonomy (Avolio et al., 2009). Although effective, democratic leadership fashion has certain disadvantages. When roles are not clearly defined and time is limited, this leadership style tin lead to failures. Farther, in some cases, members of the group might lack the expertise and cognition to contribute towards controlling. Democratic leadership style is useful if members willingly share their expertise and cognition. Also, conclusion making nether the autonomous leadership style crave a lot of time.
Laissez-Faire Leadership Style: In this leadership style, leaders are not involved with their subordinates or followers. This style is characterized past the absence leadership style. Laissez-faire leaders exercise not make group-associated decisions and policies. Subordinates or followers are responsible for making all the decisions and solving problems. Laissez-faire leaders exercise not have authority or take little authority within their system. The major functions of this leadership style include trusting members to brand appropriate decisions and hiring the trained employees. The part of this leadership way includes problem solving and cocky-monitoring along with producing quality products and services. Laissez-faire leaders are highly successful and their followers are cocky-directed as they are not critically instructed past their leaders at every step.
This leadership manner is suitable for organizations that take long-term employees. It is, however, non suitable for environments that require management, quick feedback and praise (Uhl-Bien & Marion, 2009). The disadvantages of this style include lack of awareness, equally it leads to poorly defined work roles. The leader provides minimal guidance, due to which group members are often non sure of their job roles and responsibilities.
Dynamic Leadership Mode: This is a dual-focused grade of leadership style that is adaptive in nature. This leadership style changes and reacts to different situations. The theory of dynamic leadership holds that a leader should use a fluid style of leadership to adjust according to the squad that is being led. Dynamic leadership helps improve squad motivation, equally dynamic leaders are characterized by effective action, focused energy and benevolent compassion. Farther, dynamic leaders focus on engaging with employees in such a style that success is not based on any ane private, merely the entire team. This particularly helps to motivate teams, as they experience a sense of recognition of their contribution to the overall success. Dynamic leaders are adaptive leaders, who find opportunities in obstacles take effective action during difficult times and take risks (Yoakley et al., 2014). Further, adaptive leadership creates a sense of purpose that is shared among team members. Team members experience motivated because adaptive leaders inspire and influence them rather than just demonstrating hierarchical command and control. Dynamic leaders are appreciative of teams and the contribution of each employee; they are supportive of employees in different situations, are caring, fair, humble and inspiring. All these characteristics assistance a dynamic leader motivate teams rather than but individuals (Mostovicz, 2009).
Dynamic leadership is an important resource for organizations that must operate in a highly competitive and dynamic business environment. Such leaders need to be both adaptive and flexible to operate according to the changing business organization environment (Wiesenthal et al., 2015). However, dynamic leadership lonely will not exist able to motivate individuals and team members because leaders must manage conflicts and make tough decisions. In today'south business environment, leaders face many difficulties and the pressure of producing new leadership. In the by, leadership could evolve over time, merely this is not possible now. Today's healthcare environment is highly mobile and dynamic leadership alone is not sufficient to manage the business and employees effectively. Successful organizations worldwide are adopting a proactive and intentional approach to develop leadership that is constant and competitive. Dynamic leadership includes development training and advice (Avolio et al., 2009). Farther, in a healthcare organization, a dynamic leader must accept actions that involve huge risks and create a sense of purpose amidst team members, while managing them with inspiration and influence.
Organisational Civilization Dynamics
Organizational culture is dynamic and circuitous. It can be defined every bit the pattern of shared basic assumptions learned by a group to solve the problems associated with internal integration and external adaptation. In the current competitive and dynamic business concern environment, the culture of organizations is dynamic and fluid (Fleury, 2014), as a number of cultural dynamics are at play at any given point of fourth dimension. The dynamics of organizational culture besides result from cultural systems being expressed and communicated in a diversity of means (Schneider & Somers, 2006).
The concept of civilisation is a major aspect of folklore and anthropological studies. Schein (1985) known for pioneering work in the field of organizational culture, suggests that culture is a ready of bones assumptions devised and discovered by a group. These assumptions are associated with learning to deal with external problems. Schein (1985) articulated a three-level dynamic model for culture, which needs to be learned, communicated and modified. The three levels information technology exists are artefacts (surface level); values (beneath artefacts) and basic assumptions (form the cadre). In this linear model, assumptions correspond the belief arrangement of human nature and reality, which is taken for granted. Further, values are the espoused goals and social principles that take intrinsic worth. Artefacts are the tangible, aural and visible outcomes of activities that are embedded in the values and assumptions (Schneider & Somers, 2006).
Schein (1985) farther suggests that employees working in an arrangement may share basic assumptions and values. Therefore, the studies associated with organizational culture should include the observation of artefacts that are visible, along with the interactions between people in the arrangement. Every bit such, the term cultural dynamics has originated from cultural anthropology (Hatch, 1993).
Human relationship between Dynamic Leadership and Organizational Culture
In the currently competitive and rapidly irresolute environs, healthcare organizations are concerned with choosing their leadership styles. Healthcare systems are made up of unlike professional groups, specialties and departments, along with intricate, non-linear interactions between them. Interactions in a healthcare organization are circuitous in nature. Therefore, leadership in a healthcare organisation has to capitalize on the organizational multifariousness, along with using resource optimally while working towards achieving the common goals. In a healthcare organization, there are different leadership approaches that tin be adopted to operate in this complex surroundings. The dynamics of organizational culture in terms of leadership is an of import chemical element that can exist used by a leader to grow a dynamic culture. In a healthcare organization, leadership initiates the process of culture formation past imposing expectations and assumptions on people in the arrangement. According to Schein, shared assumptions are embedded and integrated into the dynamic of the organizational culture and are managed effectively (Schneider & Somers, 2006). A dynamic leader achieves success past consistently sending clear signals about his or her priorities, values and beliefs in the business organisation surround. One time employees in a healthcare organization accept the culture, information technology becomes a strong and dynamic tool to communicate the organizations' values and beliefs, peculiarly to new members. The success of a leader will depend largely on the understanding and knowledge of the dynamics of organizational culture. A leader who understands the dynamics of the organizational culture will exist able to predict the outcomes of decisions to prevent anticipated consequences (Madu, 2012).
Relationship between Organizational Civilization Dynamic and Squad Motivation
Motivation is a major force that helps allocate the efforts associated with generating and implementing ideas that are innovative and crucial for organizational success. In a healthcare organization, culture has competing variables. The alien needs of families, institutions, providers and regulators, volition create inconsistencies. The dynamics of organizational civilization are important in a healthcare organization as they maximize a high-performance culture that motivates teams to perform effectively (Dulaimi & Hartmann, 2006). In addition, motivation levels meliorate past maximizing potential, play and purpose amidst teams. The dynamics of organizational culture are the operating arrangement of an organization. Leaders are the most important part of the system, as they assistance to build and maintain a culture that drives employee performance, motivates innovative improvements along with new solutions that encourage teams to be innovative. Further, a dynamic organizational culture fosters communication, immediate feedback, the flow of implicit cognition and initiation of innovative projects. The employ of an constructive advantage and incentive system enhances team motivation (Dulaimi & Hartmann, 2006).
Relationship between Dynamic Leadership and Dynamic Team Motivation
Dynamic leaders recognize the path they must follow to achieve their goals, along with motivating their teams. A dynamic leader usually rewards the squad intrinsically rather than extrinsically. In a healthcare organization, the staff and professionals must exist strongly motivated to generate important changes. Dynamic leadership is required for functions such equally encouraging the nursing staff and other employees to perform effectively and to make them feel valued and perceive their jobs are worthwhile. A dynamic leader, co-ordinate to the leadership theories of Alderfer's growth needs, Maslow'southward need for self-appearing and McClelland'south need for power, is driven by the need for achievement and success (Sohmen, 2013). Such leaders have a positive attitude that helps motivate the team to deal with complex situations and tasks. Moreover, likewise beingness positive, a dynamic leader must also change the squad'southward negative experiences into growth experiences that will eventually motivate the team (Sohmen, 2013). A dynamic leader also knows that each member of the team is equally important for the organizations' success; therefore, the leader focuses on motivating each squad fellow member individually to achieve the all-time results. Respecting the abilities of each team member is the priority as this farther helps to motivate the team. Encouragement from a leader improves the overall abilities of the team. For a team that intends to achieve success, cipher can substitute effective dynamic leadership. Further, in sports, the major deviation between a successful and unsuccessful team is the effectiveness of dynamic leadership. A perfect residuum between effective dynamic leadership and a motivated team is crucial for positive organizational outcomes in healthcare organizations (Sohmen, 2013).
Methods
Conceptual Framework
This written report investigates the perceived human relationship between leadership styles and team motivation levels in Abu Dhabi's healthcare sector. Specifically, the study investigates the human relationship the three leadership styles (disciplinarian, democratic and laissez-faire) accept with team motivation (Chaudhry, 2012). This also includes an analysis of the relationship between organizational culture and leadership style to provide insights into whether Abu Dhabi's healthcare sector allows leaders to follow the recommended leadership styles and how these leadership styles could be adapted into the existing culture of the organization (Almansour, 2012).
An overview of the leadership styles used in this study is shown in Table i.
| Table 1 Overview of Leadership Styles | |||||
| Dynamic Leadership | Team Motivation | Area of Involvement | Managerial Applicability | Best For | |
| High | Low | ||||
| Democratic | + | Entrepreneurial sector | Meets challenges when companies need to brand decisions over a brusk period. | Maybe lengthier decision-making procedure, the leader can appear uncertain. | Experts who know their chore and carry out their responsibilities with minimal supervision: •Pharmaceutical industry •High-tech firms •Housing construction sites •Universities •Data applied science companies |
| Geographical area | UK (casual leadership) | A consensus rule would piece of work best In Asian cultures, but complicate the process further | |||
| Workforce technical innovation | Helps employees accept changes, because they play a part in the process. | Values the input of team members and peers, but the responsibility of making the last conclusion rests with the participative leader. | |||
| Authoritarian | + | Entrepreneurial sector | Streamlined determination making nether emergency situations, equally no i challenges decisions. | Managers possess total authority and impose their will on employees, leading to abuse. | Industries with high productivity and turnover rates: •Music •Restaurants •Manufacturing |
| Geographical area | French republic favours this style of leadership | Germany (hierarchy, consensus) | |||
| Workforce technical innovation | Benefits employees who require close supervision. | Creative employees who thrive in teams hate it. | |||
| Laissez-faire | - | Entrepreneurial sector | Lacks directly supervision of employees and fails to provide regular feedback to those nether supervision. | Produces no leadership or supervision efforts from managers, which can lead to poor production and control and increasing costs | Companies either in the incubator phase of production development or engaged in highly creative businesses: •Offset-ups or social media companies •Research and development departments •High-tech firms •Product design companies •Advertising agencies |
| Geographical area | Australia (i of the mates) | Sweden (primus inter pares) | |||
| Workforce technical innovation | Platonic for highly experienced and trained employees. | Hinders the production of employees needing supervision. | |||
Research Questions
The following are identified every bit the suggested research questions:
1: What is the importance of agreement different leadership styles that may appear in the work identify?
2: What are the implications of leadership style on team motivation?
3: How practice team motivation levels influence efficiency and effectiveness at piece of work? What is the role of leadership style in improving employee performance and productivity?
iv: How does culture affect leadership style when linked to squad motivation?
Suggested Hypotheses
The following hypotheses are posited and their human relationship illustrated in Figure i. The independent variables are the three leadership styles discussed to a higher place. They are affected by culture and influence team motivation. The proposed framework likewise suggests that this study determines whether and how organizational civilisation is associated with the execution of a leadership way to accomplish an advisable level of motivation between members of the organisation.
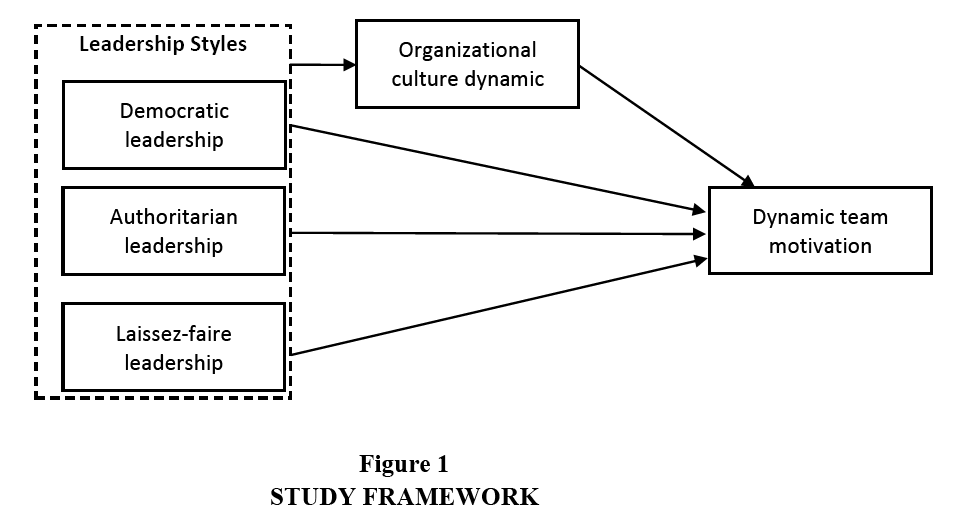
Figure ane: STUDY FRAMEWORK
H1: Democratic leadership style is positively correlated with squad motivation.
H2: Authoritarian leadership way is positively correlated with team motivation.
H3: Laissez-faire leadership style is negatively correlated with squad motivation.
H4: The dynamics of organizational culture prove a relationship with leadership styles and team motivation.
H5: Different leadership styles display significantly different levels of team motivation.
Conclusion
This study has examined the impact of different leadership styles on employee motivation focusing on dynamic leadership, which is a new concept. Leadership is an important perception that influences and motivates individuals and teams. Moreover, the focus of this report is the healthcare industry, which has complex interactions and leadership plays an important part in motivating staff. In healthcare organizations, there are different types of challenges that providers face, as their organizations be in a complex environment. Two such challenges are the changing and diverse needs of patients and exceeding the expectations of patients, along with managing the event of high costs of treatments and interventions. Team motivation thus plays a crucial office in a healthcare organization. The literature review showed that not-financial rewards are an important and constructive way of motivating teams in healthcare organizations. Teams specifically demand the support and encouragement of a leader. Therefore, the efficiency and potential of a leader has a big impact on the motivation levels of a squad. Further, in the electric current business organisation environment, there is a need for dynamic leadership and leaders have to exist adaptable and flexible to operate finer. Major leadership styles such as transformational, transactional, authentic and servant styles influence team motivation. The transformational, accurate and servant leadership styles are positively correlated with team motivation whereas transactional leadership style is constitute to be negatively correlated. It is recommended that leaders focus on leadership styles that help to motivate squad members. Squad motivation is seen as an inherent reality for organizations because multi-professional teams will be required to collaborate and work on circuitous projects. Leadership will always exist a crucial element that will guide grouping members in a healthcare organization towards specific goals. The dynamics of organizational civilization can facilitate the human relationship between leadership style and team motivation in healthcare organizations. Leadership and squad motivation are important aspects of the healthcare industry and can go along workers happy and satisfied.
Implications and Futurity Research Telescopic
This study provides an effective framework for determining the association between different leadership styles and team motivation in the healthcare sector. The framework also focuses on the dynamics of organizational culture and team motivation. Hence, this newspaper provides opportunities to ameliorate team motivation in healthcare organizations. In addition, the newspaper establishes a clear link betwixt leadership manner (democratic, authoritarian and laissez-faire) and squad motivation. Future studies can focus on developing other frameworks for investigating the relationship betwixt aspects such every bit leadership style and employee satisfaction and happiness. In this context, researchers tin use both qualitative and quantitative studies. This will assistance to investigate the profound details of leadership styles and their impact on the various aspects of organizations.
References
Almansour, Y.M. (2012). The relationship between leadership styles and motivation of managers conceptual framework. Journal of Arts, Science andCommerce, three(1), 161-166.
Al-Sawai, A. (2013). Leadership of healthcare professionals: Where do nosotros stand? Oman Medical Periodical, 28(4), 285-287.
Avolio, B., Walumbwa, F. & Weber, T.J. (2009). Leadership: Current theories, research and time to come directions. Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 421-449.
Bahmanabadi, South. (2015). A Example Study of the Impact of Leadership Styles on Bank Employees' Job Satisfaction. Unpublished Bachelor's thesis, Södertörn academy, Huddinge, Sweden.
Burns, J.P. (2001). Complexity scientific discipline and leadership in healthcare. Periodical of Nursing Administration, 31(10), 474-448.
Burns, J.P. (2001). Complexity science and leadership in healthcare. Journal of Nursing Assistants, 31(10), 474-482.
Burton K. (2012). A study of motivation: How to become your employees moving. Direction, three(2), 232-234.
Butler, P.W. (2008). Using leadership development programs to improve quality and efficiency in healthcare. Journal of Healthcare Management, 53(5), 319.
Chaudhry, A.Q. (2012). Touch on of transactional and laissez faire leadership way on motivation. International Journal of Business concern and Social Scientific discipline, 3(seven), 258-264.
Clark, R.E. (2013). Enquiry-tested squad motivation strategies. Performance Improvement, 44(1), 13-16.
Dulaimi, M. & Hartmann, A. (2006). The role of organizational civilization in motivating innovative behaviour in structure firms. Structure Innovation, 6(three), 159-172.
Enbom, J., Gustafsson, S. & Larsson, A. (2005). How coaches motivate teams?. [Online] Diva Portal Available at: http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/become/diva2:1024333/FULLTEXT01.pdf [Accessed 20 March 2017].
Epstein, N.E. (2014). Multidisciplinary in-hospital teams ameliorate patient outcomes: A review. Surgical Neurology International, 5(vii), S295-S303.
Fleury, M.T.L. (2014). Organizational culture and the renewal competences. Brazilian Administration Review, 6(1), 1-14.
Gopal, R. & Chowdhury, R.G. (2014). Leadership styles and employee motivation: An empirical investigation in a leading oil company. International Journal of Inquiry in Business organization Management, two(5), 1-10.
Greenfield, D. (2007). The enactment of dynamic leadership. Leadership in Health Services, 20(3), 159-168.
Hall, R.I. (1999). A study of policy formation in complex organizations: Emulating group decision-making with a simple artificial intelligence and a arrangement model of corporate operations. Periodical of Business Inquiry, 45(2), 157-171.
Hamidifar F. (2009). A written report of the relationship between leadership styles and employee job satisfaction at Islamic Azad University Branches in Tehran. Tehran: Iran.
Hanson, Due west.R. & Ford, R. (2010). Complexity leadership in healthcare: Leader network awareness. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, two(4), 6587-6596.
Hatch, M.J. (1993). The dynamics of organizational culture. The Academy of Management Review, 18(four), 657-693.
Humphrey, Due south.E., Morgeson, F.P. & Mannor, M.J. (2009). Developing a theory of the strategic core of teams: A part composition model of team performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(1), 48-61.
Korner, M. (2010). Interprofessional teamwork in medical rehabilitation: A comparison of multidisciplonary and interdisciplinary team approach. Clinical Rehabilitation, 24(eight), 745-755.
Körner, M., Wirtz, M.A., Bengel, J. & Göritz A.S. (2015). Relationship of organizational civilisation, teamwork and chore satisfaction in interprofessional teams. BMC Health Services Inquiry, 15(one), 243.
Leggat, S.Yard. (2007). Effective healthcare teams crave effective team members: Defining teamwork competencies. BMC Health Services Inquiry, seven(1), 17.
Lemieux-Charles, L. & McGuire, Due west.L. (2006). What do we know well-nigh wellness care squad effectiveness? A review of the literature. Medical Care Research and Review, 63(iii), 263-300.
Lichtenstein, B.B. & Plowman, D.A. (2009). The leadership of emergence: A circuitous systems leadership theory of emergence at successive organizational levels. The Leadership Quarterly, 20(4), 617-630.
Madu, B.C. (2012). Organization culture as driver of competitive advantage. Journal of Academic and Business organization Ethics, 3(4), ane-9.
Manser, T. (2009). Teamwork and patient safety in dynamic domains of healthcare: A review of the literature. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 53(ii), 143-151.
Millward, L.J. & Bryan, M. (2005). Clinical leadership in wellness care: A position statement. Leadership in Health Services, 18(2), 13-25.
Mostovicz, I. (2009). A dynamic theory of leadership development. Leadership and Organisation Development Journal, 30(6), 563-576.
Murphy, L. (2005). Transformational leadership: A cascading chain reaction. Journal of Nursing Management, 13(2), 128-136.
Negreiros, F.D.D.S. (2017). Multi-professional team's perception of nurses' competences in liver transplantations. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem, 70(ii), 242-48.
Oliver, S. (2006). Leadership in health intendance. Musculoskelet Care, 4(1), 38-47.
Osborn, R.N. & Hunt, J.Grand.J. (2007). Leadership and the choice of social club: Complication and hierarchical perspectives near the edge of anarchy. The Leadership Quarterly, 18(4), 319-340.
Penprase, B. & Norris, D. (2005). What nurse leaders should know well-nigh circuitous adaptive systems theory. Nursing Leadership Forum, 9(three),127.
Pershing, Yoakley & Associates (2014). Dynamic Leadership for Dynamic Times.
Poulton, B.C. & West, M.A. (1999). The determinants of effectiveness in primary health care teams. Journal of Interprofessional Care, 13(one), 7-18.
Rose-Grant, 50. (2016). Exploring the relationships betwixt leadership styles and job satisfaction amongst employees of nonprofit organizations. [Online] ProQuest Dissertations Publishing Available at: http://adezproxy.adu.ac.ae/docview/1798478720?accountid=26149 [Accessed i October 2016].
Schein, E.H. (1985). Organizational culture and leadership. São Francisco: Jossey Boss.
Schneider, M. & Somers, One thousand. (2006). Organizations as complex adaptive systems: Implications of complication theory for leadership research. The Leadership Quarterly, 17(4), 351-365.
Schreiber, C. & Carley, Yard.M. (2008). Network leadership: Leading for learning and adjustability. In M. Uhl-Bien and R. Marion, eds. Complexity Leadership, Role I: Conceptual Foundations. Information Historic period Publishing. 291-332.
Sohmen, V.S. (2013). Leadership and teamwork: Ii sides of the same coin. Journal of It and Economic Development, four(2), 1-18.
Strasser, D.C., Falconer, J.A., Herrin, J.S., Bowen, S.E., Stevens, A.B. & Uomoto, J. (2005). Team functioning and patient outcomes in stroke. Athenaeum of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 86(3), 403-409.
Tsai, Y. (2011). Relationship between organizational culture, leadership beliefs and job satisfaction. BMC Health Services Research, 11(1), 98. Available at: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6963/xi/98 .
Tzenalis, A. & Sotiriadou, C. (2010). Health promotion as multi-professional and multi-disciplinary work. International Journal of Caring Sciences, 3(2), 49-55.
Uhl-Bien, 1000. & Marion, R. (2009). Complexity leadership in bureaucratic forms of organizing: A meso model. The Leadership Quarterly, 20(four), 631-650.
Uhl-Bien, M., Marion, R. & McKelvey, B. (2007). Complication leadership theory: Shifting leadership from the industrial age to the knowledge era. The Leadership Quarterly, xviii(4), 298-318.
Wiesenthal, A.M., Kalpna, J., McDowell, T. & Radin, J. (2015). The new md leaders: Leadership for a dynamic wellness. The New England Journal of Medicine, 1-3.
Zachariadou, T., Zannetos, S. & Pavlakis, A. (2013). Organizational culture in the primary healthcare organization of republic of cyprus. BMC Health Services Research, thirteen, 112.
Source: https://www.abacademies.org/articles/the-effects-of-leadership-styles-on-team-motivation-6793.html
0 Response to "The Art of Motivating a Group of People to Act Towards Achieving a Common Goal âââ€susan Ward"
Post a Comment